Choosing the Right Insecticide for Rice Bug Management
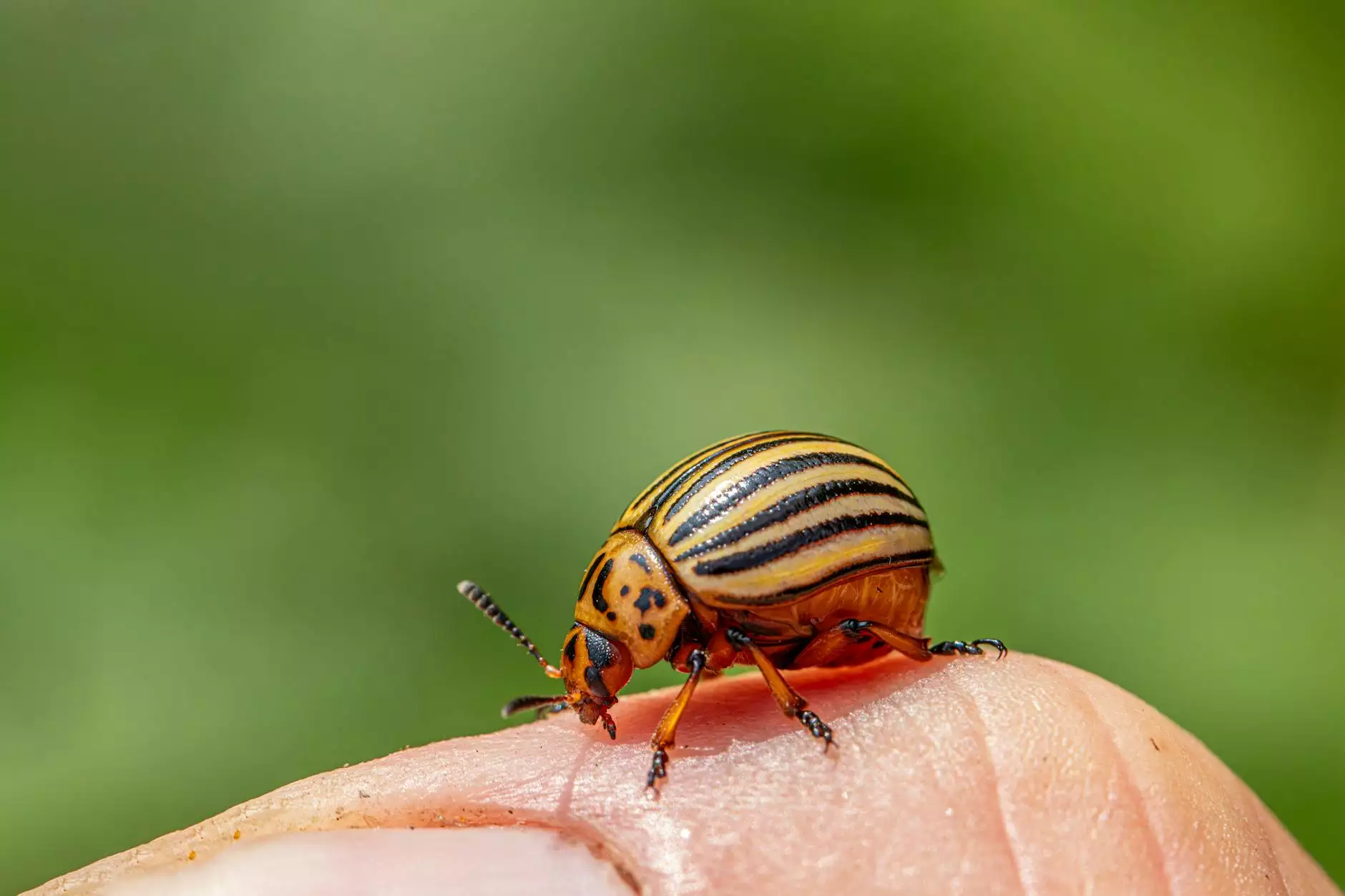

Rice, a staple food for over half of the world's population, is often threatened by various pests, among which the rice bug is particularly notorious. Farmers striving to achieve optimal yield must prioritize effective pest management. One of the most critical components in this battle is selecting the right insecticide for rice bug control. This article delves into the various strategies, products, and practices to ensure a successful defense against these destructive nuisances.
Understanding the Rice Bug
The rice bug, scientifically known as Leptocorisa spp., is an emerging threat to rice crops, particularly in Asian countries. Adult rice bugs are known for their distinctive elongated bodies and powerful sucking mouthparts, enabling them to extract sap from rice plants. This feeding behavior results in several physiological problems, including:
- Reduced plant vigor
- Stunted growth
- Lower grain quality
- Increased vulnerability to diseases
Importance of Using Insecticides
The timely application of an appropriate insecticide for rice bug management can significantly diminish the impact of these pests. The use of effective chemical solutions helps to:
- Protect the rice plants during critical growth stages
- Enhance the quality and yield of rice crops
- Reduce the economic burden caused by pest damage
Types of Insecticides for Rice Bug Control
When it comes to choosing an insecticide for rice bug control, it's vital to consider a range of products available in the market. Each category has its specific applications and effects on pests:
1. Chemical Insecticides
Chemical insecticides are synthetic products designed to target specific pests while minimizing harm to crops. Some popular classes include:
A. Pyrethroids
These insecticides are known for their rapid action and are effective against a broad spectrum of insect pests.
B. Neonicotinoids
Neonicotinoids act on the nervous system of insects, effectively incapacitating them. They have low toxicity to humans and animals when applied as directed.
C. Organophosphates
This class of insecticides works by inhibiting essential enzymes in the insect’s nervous system, leading to paralysis and death.
2. Biological Insecticides
Biological options utilize natural organisms or substances that target pests selectively. Some well-known biological insecticides include:
A. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)
Bt is a bacterium that produces toxins harmful to certain insect larvae, including some species of rice bugs.
B. Neem Oil
Extracted from the seeds of the neem tree, neem oil disrupts the feeding and breeding of a wide range of insects, including rice bugs, serving as both an insect repellent and growth regulator.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Insecticide
Selecting the correct insecticide for rice bug management requires careful consideration of several factors:
1. Crop Safety
Before applying any insecticide, it is crucial to assess its safety for the rice variety being cultivated. Always check product labels to ensure compatibility.
2. Environmental Impact
Consider using insecticides that have lower environmental toxicity, particularly if you’re operating in sensitive ecosystems or near water sources.
3. Pest Resistance Management
To avoid the development of resistance in rice bug populations, rotate insecticides with different modes of action, ensuring continued effectiveness.
4. Timing of Application
The timing of insecticide application is crucial for successful pest management. Target applications around:
- Peak pest populations
- Critical growth stages of rice
Application Methods for Insecticides
How you apply the insecticide can be just as important as what you apply. Consider the following application methods:
1. Spraying
Foliar applications through backpack or tractor-mounted sprayers are common. Ensure that the entire plant surface is adequately covered for optimal absorption.
2. Seed Treatment
Some insecticides can be applied as a seed treatment, providing early protection as seeds germinate and plants grow.
3. Soil Application
Select products designed for soil application that can act systemically, enhancing protection from the ground up.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
While having a reliable insecticide for rice bug is critical, it’s equally important to develop an integrated approach. IPM strategies can improve overall pest management by combining multiple techniques:
1. Cultural Practices
Implement agronomic practices such as crop rotation, proper irrigation, and timely planting to minimize the risk of pest outbreaks.
2. Monitoring and Scouting
Regularly monitor rice fields for signs of rice bugs. Early detection can result in timely interventions, reducing reliance on chemical treatments.
3. Use of Resistant Varieties
Planting rice varieties that are resistant to specific pests can greatly reduce the need for insecticides.
Preventive Measures
Implementing preventive measures can significantly lower the risk of rice bug infestations:
- Maintain proper field hygiene: Remove crop residues that can harbor pests.
- Encourage beneficial insects: Natural predator populations can help control pest numbers.
- Utilize trap crops: Planting pest-attracting crops can divert rice bugs away from the main rice field.
Conclusion
In summary, effective management of the rice bug through the strategic use of insecticide for rice bug control is essential for maintaining high-quality yields. By understanding the pest, choosing the right insecticide, and adopting integrated pest management strategies, rice farmers can significantly reduce losses and maintain their livelihoods. As we advance into a future facing numerous agricultural challenges, enhancing our pest management approaches will be vital to safeguarding our food sources.
Visit tsgcinc.com for more information on pest management solutions and farming equipment. Explore various options for maintaining the health and productivity of your agricultural ventures.